According to new research conducted at the University of California, we are closer to implanting new thoughts, memories, and sensory experiences in the brain.
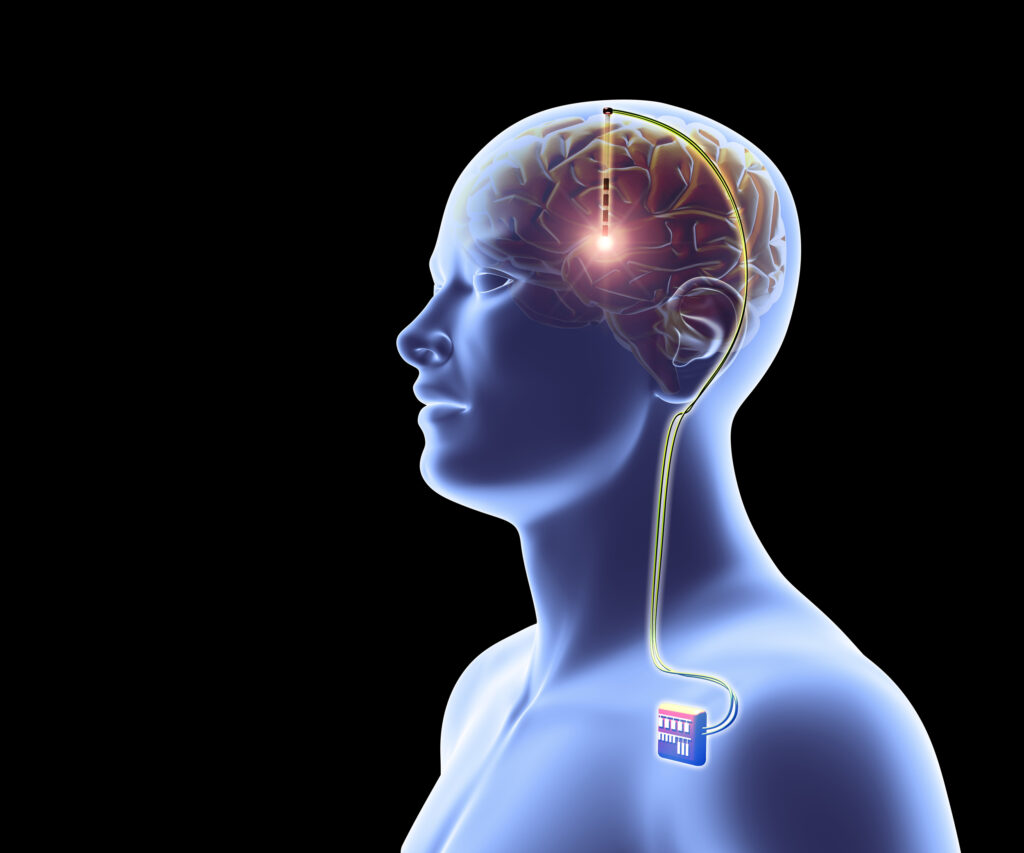
Neural programming is a concept that allows artificial modification of brain activity. It could input, modify or delete memories or even create a sensory experience. The idea is not new, but it has mainly remained in the realm of fantasy and science fiction. However, a group of scientists has succeeded in creating a technique that could activate and deactivate several neurons by projecting holograms to the brain.
The technique has been renamed “holographic brain modulation” and involves the use of light to alter brain function. It achieves this by projecting holographic images into brain cells. The holographic images trick the brain into believing something that is not there.
How Does The Holograph in the Brain Work?
The flashes produced by the holographic device act as tiny control units for stimulating the brain’s neurons. It effectively simulates life experiences and events that have never occurred in reality. The holograms in the brain could allow dynamic neural editing to modify memory, suppress pain, or even introduce new images to the brain. The technology is known as a holographic brain modulator and uses a holographic projector to control neural activity. The aim is to control thousands of neurons at the same time to create new memories or sensations.
What will be the benefits of holographic projection in the brain?
Scientists are optimistic that the technique could have varied applications. It could help patients with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) to overcome negative and harmful experiences by artificially replacing them with positive ones. This technology could help blind people perceive their surroundings. It could be achieved via a camera that could convert the images taken into a neural electrical signal and feed it to the brain, acting as the optic nerve.
Alan Mardinly, cellular and molecular biologist (University of Berkeley) states that, “This technique has great potential for neural prostheses, thanks to its precision allowing the brain to interpret neural activation patterns. If you can read and write the language of the brain, then you can communicate more easily with it.”
Scientists Successfully Tested Small Holographic Implants in Mice
The technique’s effectiveness is already established as scientists successfully tested small holographic Implants in Mice. The activity focussed on creating false sensations and memories in Mice. The test confirmed that the technique work and the mice were led to believe something that was not there.