Introduction
Large language models (LLMs) combined with autonomous systems are revolutionizing various sectors like self-driving vehicles and intelligent robots. LLMs improve autonomous systems by providing natural language comprehension, decision-making, and flexibility. This helps them operate more efficiently and intelligently.
In this blog, we will look at how LLMs are altering autonomous systems, their most recent advancements, real-world applications, and what the future holds. We will also explore the potential ethical implications of using LLMs in autonomous systems.
How LLMs Are Powering Autonomous Systems
Autonomous systems use AI to perceive, process, and act in changing environments. LLMs enhance this by enabling context-aware decision-making, real-time communication, and intelligent automation.
LLMs help autonomous systems understand and respond to human commands naturally. They also enable systems to learn and improve without reprogramming when faced with new situations. LLMs can integrate text, speech, vision, and sensor data to make better decisions.
AI-driven systems can analyze large data streams quickly to solve problems in real-time.
Key Applications of LLMs in Autonomous Systems
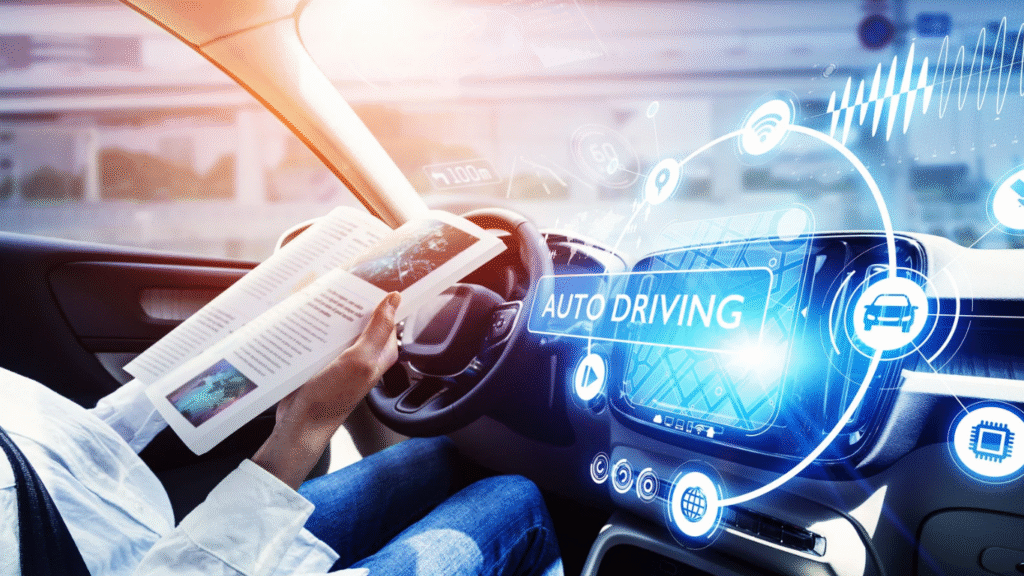
1. Self-driving vehicles
Self-driving vehicles use LLMs to process voice commands, interpret road signs, and predict driver behavior for better navigation and safety. For instance, Tesla’s AI system incorporates LLMs to enhance self-driving abilities by learning in real time.
2. AI-Powered Robotics
Robots use LLMs to understand us better, do more stuff, and act more naturally. For example, Boston Dynamics’ robots use LLMs to process verbal commands and navigate unpredictable spaces.
3. Smart Drones
Drones outfitted with LLMs can read voice commands, evaluate topography, and optimize flight paths for operations such as surveillance and delivery.Amazon’s delivery drones employ LLMs to connect with people and modify paths dynamically.

4. Industrial Automation
AI-powered robots in factories rely on LLMs for predictive maintenance, workflow efficiency, and human-machine cooperation.For example, Siemens uses LLM-powered AI to improve manufacturing operations and boost production.

5. Military & Defense
In risky areas, AI-powered robots use language models to do reconnaissance, identify threats, and make calls on the fly. For instance, AI-driven battlefield analysis tools use LLMs to process real-time intelligence data.

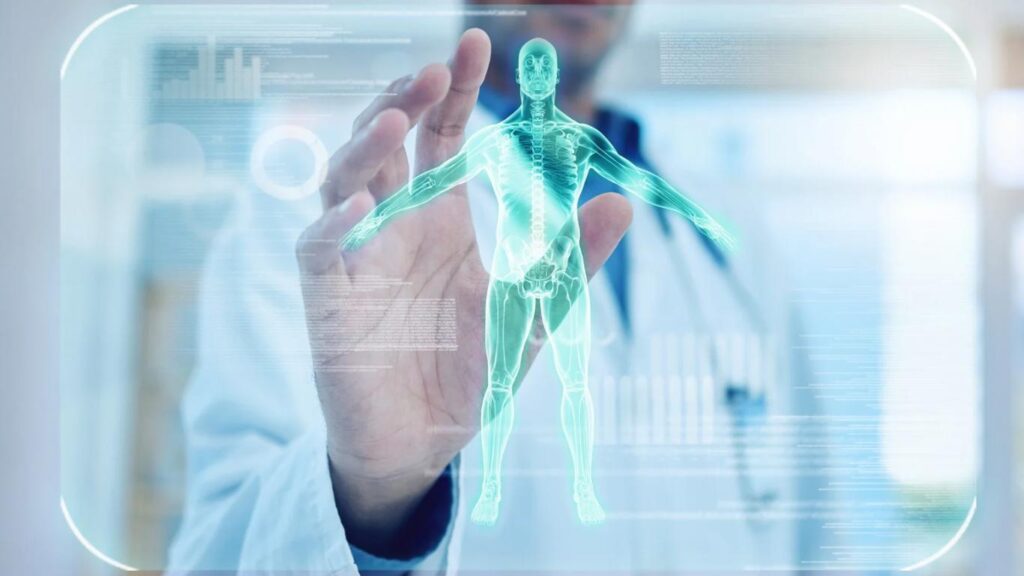
6. Healthcare & Medical AI
Autonomous medical assistants employ LLMs to diagnose ailments, provide therapies, and help with robotic procedures. AI-powered surgical robots, like the Da Vinci, employ LLMs to improve accuracy in difficult medical operations.
7. Smart Assistants & Customer Service
LLM-powered virtual agents conduct conversations, process requests, and provide assistance across several sectors.Chatbots, such as GPT-4-powered assistants, manage consumer inquiries with near-human accuracy.
Ethical Implications of Using LLMs in Autonomous Systems
The use of large language models (LLMs) in autonomous systems raises substantial ethical concerns that must be addressed to assure safety, justice, and accountability. Here are several important ethical implications:
1. Bias and Fairness
LLMs are trained on large datasets, which may contain bias. When used in autonomous systems (e.g., self-driving vehicles, drones, or robotic assistants), these biases may result in unfair or detrimental decision-making.
For example, a skewed dataset in an AI-powered surveillance system may disproportionately misidentify specific demographic groups.
In healthcare, an autonomous system utilizing an LLM may make incorrect recommendations because of underrepresented patient data.
2. Accountability and Transparency
LLMs are black-box models, making it difficult to track how a decision was taken. The lack of openness raises issues about:
Legal responsibility and explainability are crucial in AI-powered autonomous systems, ensuring developers, users, or organizations are held accountable for their decisions and can provide clear justifications.
3. Autonomy vs. Human Oversight
Autonomous systems driven by LLMs can make choices on their own, decreasing the need for human intervention. However, this can result in:
> Loss of human control: In vital sectors such as military or financial trading, unregulated AI-driven judgments may have unforeseen repercussions.
> Overreliance on AI: Users may place too much faith in autonomous systems, even if they make mistakes or require human intervention.
4. Misinformation and Manipulation
LLMs can produce persuasive but inaccurate or misleading information. In autonomous systems, this may emerge as:
Fake reports or alerts: AI-generated disinformation in security or emergency response systems can lead to confusion or fear.
Propaganda and deepfakes: Autonomous AI agents might be deployed to influence public opinion, making it difficult to discern between fact and fiction.
Challenges and Limitations
LLMs in robots face challenges such as potential biases, high computing power requirements, and potential cyber threats exploiting AI system vulnerabilities. Governments must establish rules for AI automation to ensure fairness and security.
The Future of LLMs in Autonomous Systems
- Self-Learning AI: Future autonomous systems will constantly improve their abilities with minimum human interaction.
- Human-AI Collaboration: Advanced LLMs will allow for seamless human-machine cooperation across sectors.
- Fully Autonomous Cities: Smart cities will incorporate AI-enabled transportation, energy, and security systems powered by LLMs.
- Ethical AI Governance: New frameworks will guarantee that AI is deployed responsibly in mission-critical applications.
Conclusion
Large language models are reinventing autonomy in technology, making AI-powered systems smarter, more adaptive, and engaging. As improvements continue, LLMs will usher in a new age of automation throughout sectors, pushing the frontiers of what is feasible.
To address ethical concerns about AI deployment, stricter rules, effective human-AI collaboration, transparent AI models, and bias reduction measures are required. Balancing innovation and accountability is critical for ensuring that AI improves human lives without jeopardizing safety, justice, or ethical integrity, and also ensuring AI models make explainable decisions.
What do you think? Will AI-powered autonomy transform our future? Please leave a remark below with your thoughts!



