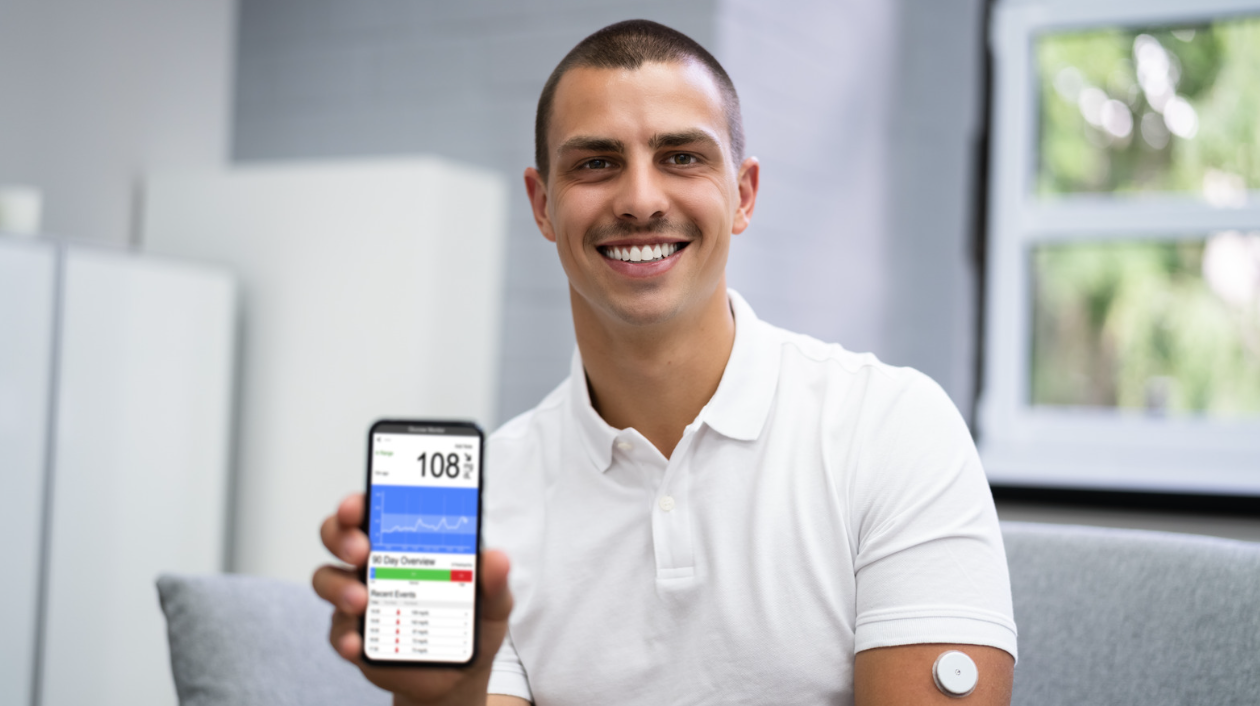
The concept of remote patient monitoring (RPM) can significantly improve the way healthcare is delivered. It would be very convenient if your healthcare providers were able to closely monitor your health without requiring you to visit a clinic.
RPM continuously monitors health signs and manages chronic health conditions remotely using the latest digital medical devices. Therefore, proactive interventions can be initiated in a timely way, which may have a positive impact on patients’ outcomes.
In this article, we will look at how RPM works, how it is beneficial, how it is challenging, and how innovative technologies are driving it forward.
What is Remote Patient Monitoring?
RPM, or Remote Patient Monitoring, is a new wave of healthcare that goes beyond hospitals and clinics. With RPM, healthcare providers can keep a close eye on patients from the comfort of their own homes, using cutting-edge digital devices.
With these innovative tools, like weight scales, blood pressure monitors, pulse oximeters, and blood glucose meters, you can collect important health data and send it straight to your doctor.
With this model, patients get personalized care and attention without having to make repeated visits to the physician’s office. This gives patients a more manageable and proactive approach to managing their health.
The key components of RPM
Several key components make up RPM to provide integrated monitoring and care for patients. Here’s what they are:
Wearable devices and sensors
The use of devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical devices for monitoring essential signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and glucose levels. These devices collect and transmit data continuously and regularly to healthcare providers.
Mobile health applications
The use of apps that enable patients to record symptoms, medication usage, and other health-related information. These applications offer a user-friendly interface that allows patients to interact with their healthcare providers.
Telemedicine platforms
The use of video consultation, messaging, and telephone communication tools between patients and healthcare providers, allowing for real-time communication, enables prompt resolution of patient concerns.
Data Integration and Analytics Systems
A system for centralized access to health data from multiple devices, intended for healthcare professionals. This platform allows the data to be analyzed to identify trends, predict health issues, and support clinical decision-making.
The evolution of RPM
Historically, RPM was used primarily for chronic disease management. The adoption of this method has risen due to advances in technology and the COVID-19 pandemic, which called for an alternative method of providing care. During the pandemic, RPM proved essential in managing patient care while minimizing exposure risks associated with in-person visits.
Regulatory changes
There has been an expansion in coverage of RPM services by regulatory agencies, such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). As part of this, certain requirements will be waived during public health emergencies to facilitate broader access to remote monitoring.
Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
Implementing RPM can have several benefits for patients and healthcare providers:
Enhanced patient outcomes
● Timely interventions
By continuously monitoring the patient, healthcare providers are able to detect changes in the patient’s condition promptly, allowing them to intervene in a timely manner before complications arise.
● Enhanced Chronic Disease Management
The use of RPM is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Research has shown that RPM can reduce hospital readmission rates and emergency department visits.
● Increased patient engagement
Through RPM, patients are empowered to participate in the care process. A patient can monitor their health data on a regular basis, which enhances adherence to their treatment plans and instills a sense of responsibility.
● Cost savings
The use of RPM can reduce the need for hospital visits and readmissions, which can result in substantial cost savings for healthcare systems. For example, some organizations have reported savings of hundreds of thousands of dollars after implementing RPM programs due to decreased readmission rates.
● Accessibility
RMMS provides healthcare services to patients who are unable to access traditional healthcare due to geographical or mobility limitations. The importance of this is particularly great for patients who are elderly or who live in rural areas.
Technology used in RPM
RPM works because a variety of technologies make data collection and transmission easy:
● Medical devices
In RPM, the following devices are commonly used:
➔ Blood Pressure Monitors: Keep track of your hypertension.
➔ Glucose Meters: Used for monitoring diabetic blood sugar levels.
➔ Pulse Oximeters: Used to measure the saturation level of oxygen in the blood.
➔ Wearable Fitness Trackers: Continuously monitor physical activity and physiological signs.
These devices can be connected via cellular networks or Bluetooth technology to transmit data securely.
● Data Management Systems
A combination of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Revenue Management Systems (RPMs) allows healthcare providers to effectively manage patient data. By using these systems, providers can analyze trends over time and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Implementation challenges of RPM
Despite its advantages, several challenges can hamper RPM implementation:
The technical barriers
In some cases, patients may have difficulty using medical devices or understanding how to transmit their data correctly.The only way to overcome these barriers is to ensure adequate training and support.
Threats to data security
There are concerns about privacy and security when sensitive health data is transmitted. For healthcare organizations to protect patient information from unauthorized access, robust cybersecurity measures must be implemented.
Medical Misdiagnosis Risks
The risk of clinical misdiagnosis increases if abnormal readings are not flagged appropriately or if monitoring protocols are not followed accurately. Identifying patients who need further attention is essential, and clear guidelines should be established for that.
The Best Practices for Implementing RPM
The following best practices should be considered by healthcare organizations to maximize the benefits of RPM:
Choosing patients
It is crucial to identify candidates who are suitable for RPM. A remote monitoring program is ideal for patients with chronic conditions or those who require regular monitoring.
A comprehensive training program
The technology should be thoroughly trained for both patients and healthcare staff to ensure that everyone is able to use it effectively. As part of this effort, patients are educated about how to use their devices, how to report data, and what constitutes an emergency.
Continual data monitoring
The establishment of dedicated teams to monitor incoming data will ensure that abnormal readings are addressed as soon as possible. A proactive approach promotes patient safety and improves clinical outcomes.
A look at the future of remote patient monitoring
Despite the constant advancement of technology, RPM looks promising for the future.
● AI integration
The use of artificial intelligence can enhance RPM by rapidly analyzing large datasets, identifying trends that may not be apparent from a manual review. With this capability, treatment plans could be more personalized based on the patterns of patient data.
● Acute Care Expansion
Although RPM has mainly been used to manage chronic diseases, it is gradually finding its way into acute care settings as well. Hospitals, for example, are starting to use remote monitoring systems to monitor recovery post-surgery.
● Insurance coverage increased
In the future, more insurance providers are likely to cover these services comprehensively, which will make them more accessible to a wider range of patients.
Conclusion
There is no doubt that remote patient monitoring is a huge step forward in healthcare. By using technology to watch patient health remotely, healthcare provider costs can be reduced, outcomes get better, and patient engagement gets better. In spite of implementation and data security challenges, organizations can take advantage of the benefits of RPM by adopting best practices.
As we move forward into a more digital healthcare landscape, employing technologies such as artificial intelligence and expanding insurance benefits, remote patient monitoring will likely become an integral part of modern medical practice.