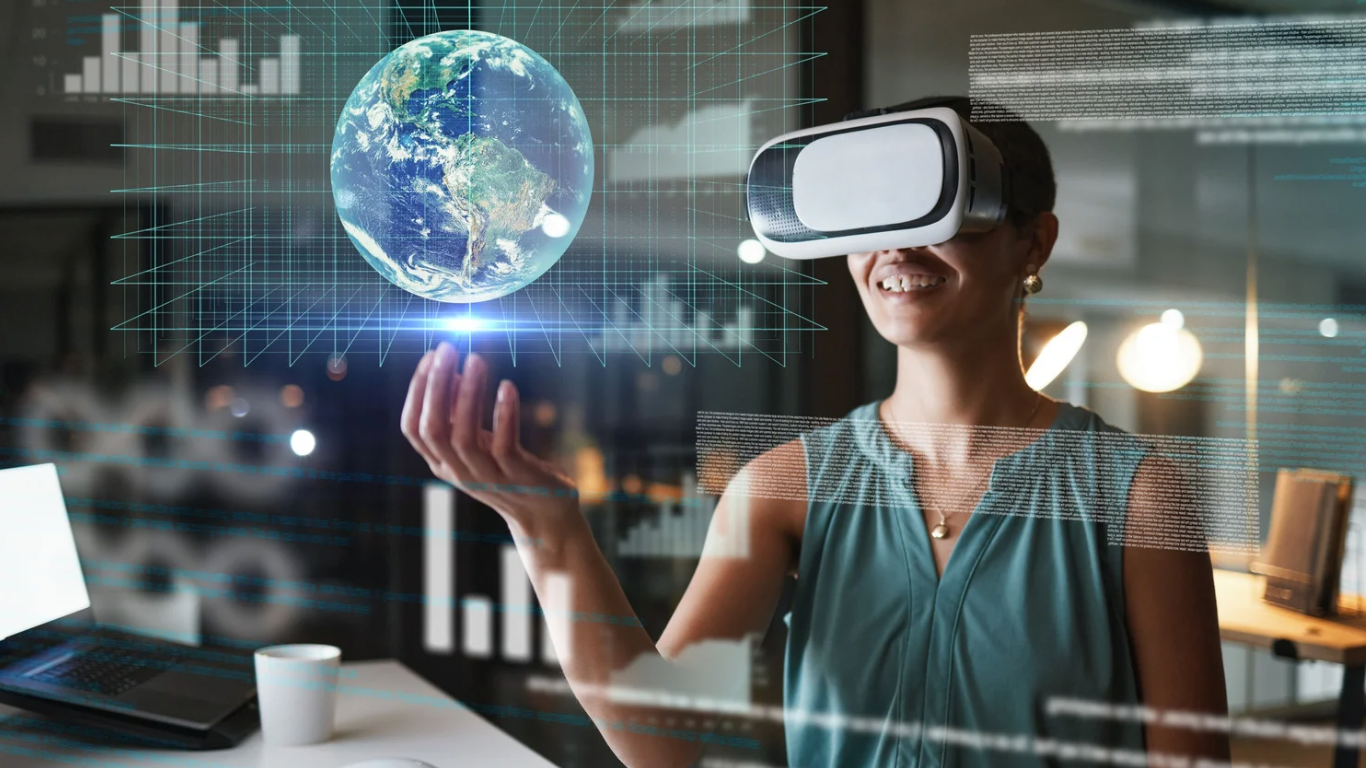
The concept of spatial computing is redefining the way we interact with the digital world, fusing the physical and the virtual in ways that were once only possible in sci-fi films, introducing new and exciting ways to interact with the digital world.
Spatial computing is bringing new waves of tech innovation, from augmented reality apps in stores to self-flying drones. So, what’s the deal with spatial computing, and why is it getting so much buzz?
What is Spatial Computing?
Spatial computing is all about using digital technology to connect with and manage our physical surroundings in a fun and engaging way. It combines the real world, the way we act, and our digital devices which allow computers to recognize and interact with our environment around us. It is like giving technology the ability to “see” and understand space just like we do.
In simple terms, spatial computing helps devices understand and interact with the world around them based on their specific location. This means you can have experiences that are aware of the context of where you are. It includes cool technologies like Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR), artificial intelligence (AI), sensors, 3D mapping, and geolocation. It’s like bringing your surroundings to life in a whole new way.
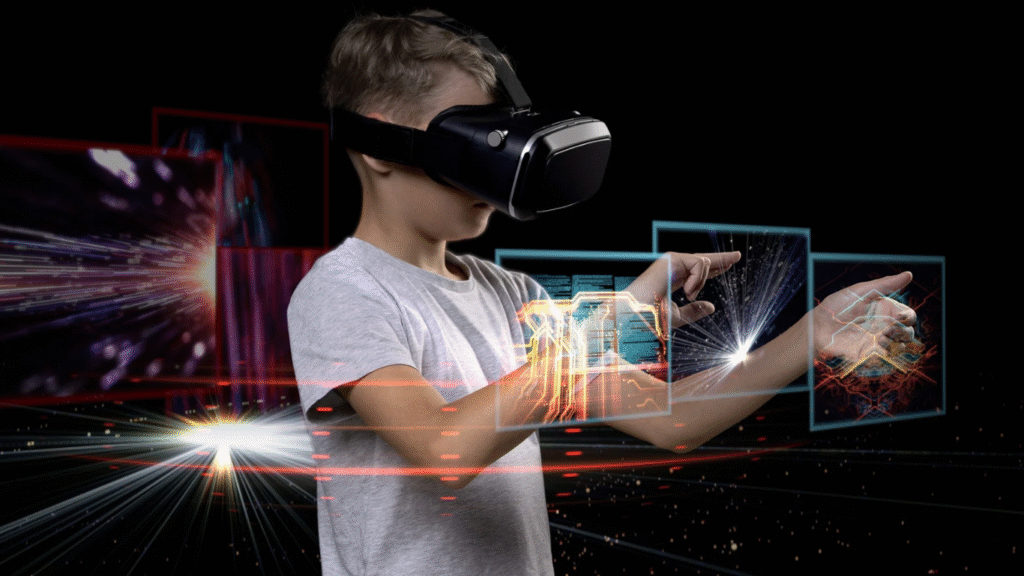

What are examples of spatial computing?
Spatial computing is a fun and exciting term that describes great tech experiences such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR).
It also includes related ideas like mixed reality and extended reality. It’s about blending the digital world with our real lives in creative ways.
- Virtual reality (VR) – An immersive visual experience that completely covers what you see in the real world and replaces it with a virtual setting.
- Augmented reality (VR) – Digital content is layered over the real world, but you can still see everything happening around you.
- Mixed reality (MR) – Digital content is layered on top of what we see in the real world, enabling the different elements to work together and interact.
- Extended reality (XR) – A general term that covers virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR).
How Does Spatial Computing Work?
Spatial computing brings together the virtual and physical worlds in a seamless way. You can experience it through headsets such as the Apple Vision Pro, Microsoft HoloLens, Meta Quest Pro, and Magic Leap. These devices display the real world and, at the same time, embed real objects into the scene in a way that appears three-dimensional. For example, you could place a virtual piece of furniture in your living room to see what it would look like before you buy it.
These devices use a mix of cool technologies to blend our digital and physical worlds. First up is computer vision, which helps them interpret data from cameras and sensors to understand what’s around them, including where things are and how they move. Then there is sensor fusion, which combines information from different sensors like cameras and LiDARs to give a clear and complete picture of the environment. Plus, they create a 3D model of the space with spatial mapping, making it super easy to place and interact with digital content in a fun and precise way!
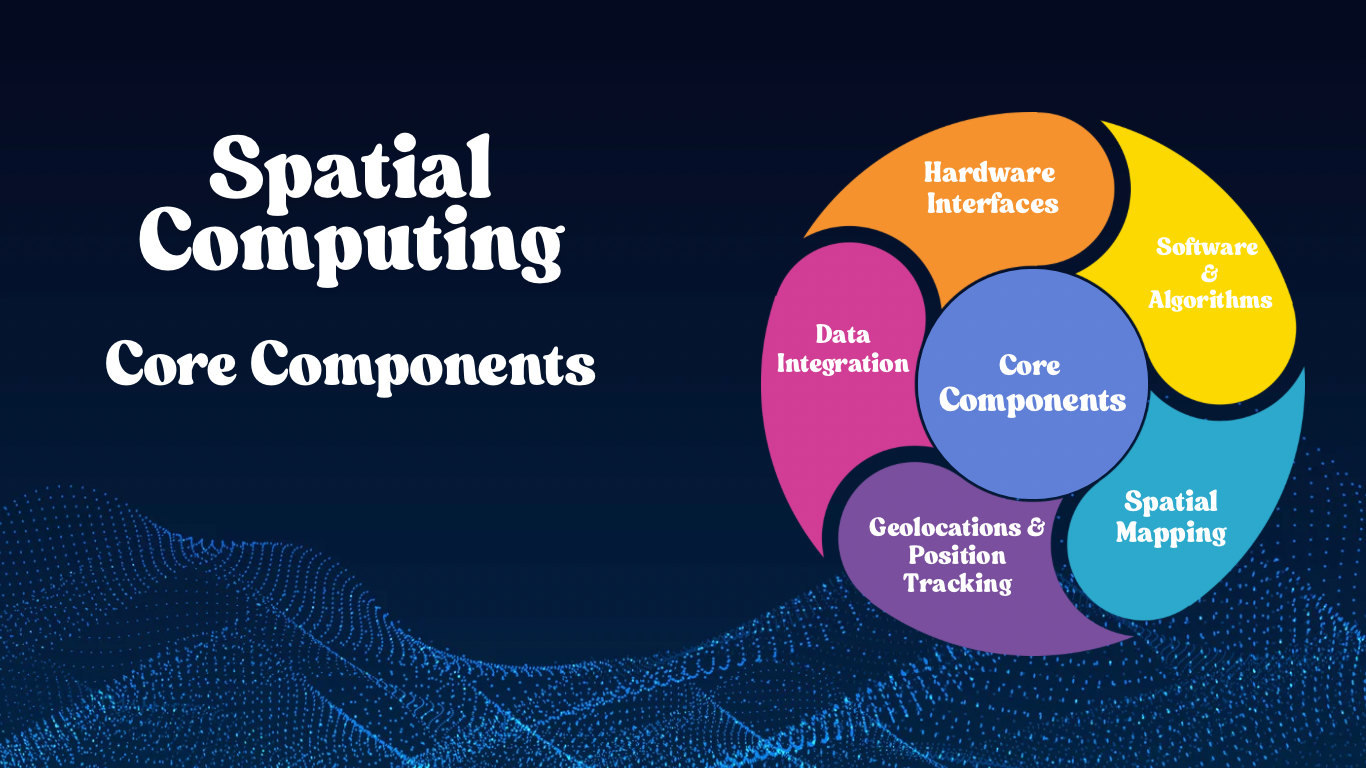
Core Components of Spatial Computing
- Hardware Interfaces – Think of all the cool gadgets we have these days, like AR and VR headsets, smart glasses, handy sensors, LIDAR technology, cameras, and wearables. All these devices let us interact with the world around us in exciting new ways.
- Software and Algorithms – Machines that use advanced technology like machine learning and artificial intelligence, along with special mapping techniques, can understand and respond to their surroundings.
- Spatial Mapping – Making 3D maps of our surroundings lets devices blend digital content seamlessly into the real world. It is a fun way to explore and interact with everything around us.
- Geolocation and Position Tracking – GPS, SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), and various tracking technologies play a crucial role in helping us figure out the precise location and direction of a user or object. They are like the friendly guides that keep us on track!
- Data Integration – Real-time data processing, cloud computing, and edge computing are fantastic tools that help us manage and make sense of the huge amounts of data gathered by spatial computing systems. They make it easier and quicker to analyze everything!
Key Applications of Spatial Computing
- Healthcare – With spatial computing, doctors can see organs in 3D before making an incision. Students can practice in a safe environment with virtual reality.
- Retail and E-commerce – Spatial computing is transforming virtual try-ons, augmented reality previews, and immersive shopping experiences. Ikea’s app for example shows how furniture fits in the room.
- Manufacturing and Industry – AR headsets give workers hands-free guidance, while digital twins (virtual replicas of physical systems) help optimize processes and predict maintenance needs.
- Gaming and Entertainment – Games like Pokémon Go and Meta Quest use spatial computing to provide immersive gameplay. Hollywood also uses it for virtual productions.
The Future of Spatial Computing
Spatial computing is still getting started, but it’s on a great path. With the exciting growth of the metaverse, digital twins, smart cities, and spatial AI, we are moving closer to a world where technology blends seamlessly with our real lives. Imagine a time when computers not only listen to us but actually “get” our surroundings. It’s an exciting future ahead.
As 5G networks develop and AI technology improves, spatial computing will become faster, more accurate, and easier to use. The use of neural interfaces and brain-computer connections could take this even further, allowing us to interact with the digital world just by thinking.



